-
09-07-2024
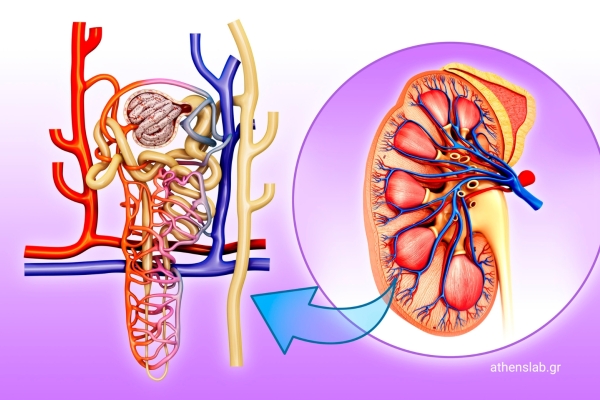
Goodpasture Syndrome
Goodpasture syndrome, or anti-GBM disease, is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by antibodies that attack the basement membrane of the glomeruli in the kidneys and the alveoli in the lungs. This autoimmune attack results in nephritis and pulmonary hemorrhage, leading to...
-
20-03-2024
Methylation and Autoimmune Diseases
Methylation plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression and maintaining genomic stability. In autoimmune diseases, aberrant DNA methylation patterns have been implicated in the dysregulation of immune responses and the development of autoimmune conditions. Methylation can...
-
17-11-2023
The Relationships between Intestinal Permeability and Target Antibodies for a Spectrum of Autoimmune Diseases
The worldwide prevalence of autoimmune diseases that have limited treatment options and preventive strategies is rapidly rising. There is growing evidence that the microbiota and the integrity of the intestinal barrier play a role in autoimmune diseases. The potential to evaluate...
-
04-08-2023
Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Testing Algorithm
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the blood-clotting process. In this syndrome, the immune system produces antibodies that target certain proteins and phospholipids (a type of fat molecule) in the blood. These antibodies can lead to...
-
23-11-2022
Multiple Sclerosis and Microbiome
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS). The disease leads to the formation of inflammatory lesions in the CNS, in which myelin sheaths break down and demyelinated axons are damaged. This leads to neurological...
-
03-10-2022
Role of the gut microbiome in chronic diseases
The gut microbiome, i.e., the community of bacteria and other microorganisms living in the human gut, has been implicated both directly and indirectly (mediating the effects of diet) on human health. The associations between gut microbiome composition and disease status have been...
-
25-05-2022
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME) / Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS)
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME), also known as Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS), is a neglected, serious debilitating disease with no proven diagnostic marker and specific therapy. While there is evidence for several pathophysiological abnormalities including the neurological,...
-
05-11-2018
New data on the relationship between autoimmune diseases and an intestinal bacterium
Can the bacteria of our gastrointestinal tract send the wrong "messages" to the body? Researchers at Queen's University in Belfast present new evidence. Researchers discovered for the first time that a specific bacterium in the gastrointestinal tract produces protein molecules...
-
07-09-2018
Rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmune diseases: What is their relationship with our gut microbiome? Why are they on the rise?
Autoimmune diseases are a modern health problem for which scientists know little about their causes. But now there are very reasonable suspicions that the role of the intestinal microbiome is crucial! Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that afflicts many people and...